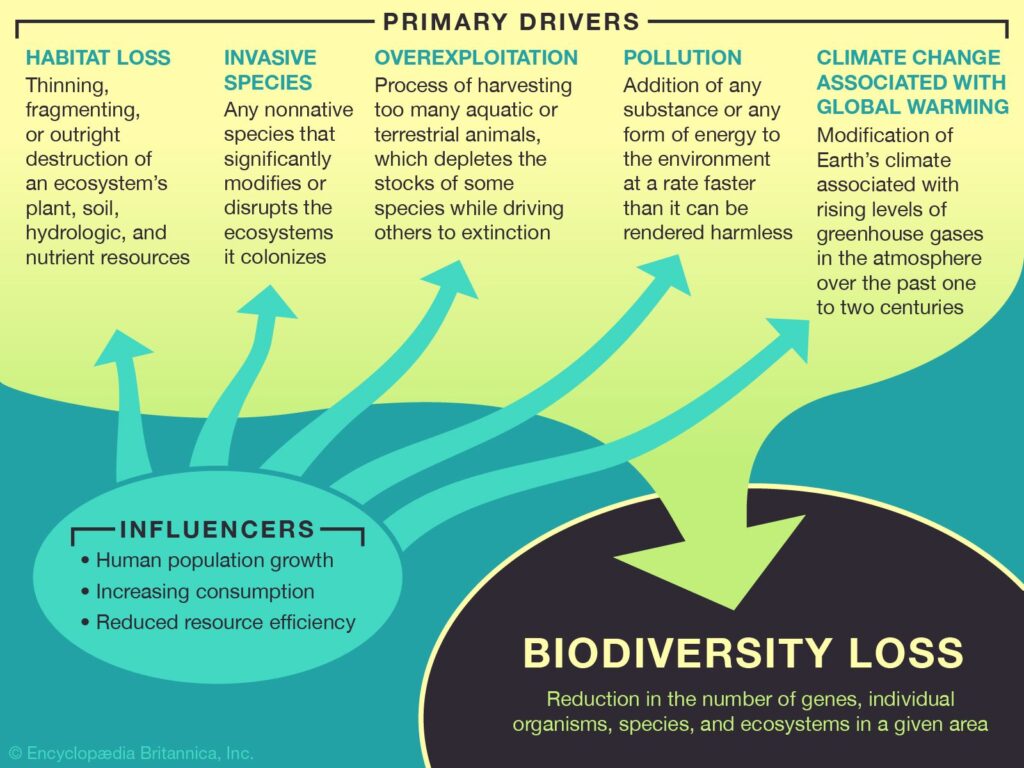
Biodiversity, a contraction of “biological diversity”, is the variety of life found in a place on Earth or, often, the total variety of life on Earth. A common measure of this variety, called species richness, is the count of species in an area. The tropics, for instance, have more biodiversity than temperate regions—but raw species count is not the only measure of diversity. Biodiversity encompasses the genetic variety within each species and the variety of ecosystems that species create.
Biodiversity remains difficult to measure precisely despite all the tools and data sources available today. There are so many factors to take into account such as the number of species in a specific zone, but this cannot be considered alone, it has to be put into its context The density of different classifications of organisms, the number of different plant functional types, the diversity of gene sequences in a sample of microbial DNA taken from the soil, as wells as the variability function, quantity and distribution, provide a good understanding of the roles of biodiversity.

Biodiversity plays an essential role in the climate locally, regionally, and globally. Any change in the biodiversity, any significant change in its components – species and habitats -, has a direct effect on ecosystems functioning and eventually on the climate. For example, if a consequential quantity of trees is cut down in a zone in a dense forest, this may cause the ecosystem to create less moistening effect on the atmosphere, resulting in less precipitation, causing these areas to become dry and less prone for trees to grow back, with the destruction of animal habitats and their extinction, for some of them – a very sad illustration is the Amazon Forest.
Biodiversity of Mauritius
Although Mauritius is a very small island (1865 sq. metres), it is recognised as one of the world’s biodiversity hotspots. The flora and fauna of Mauritius have a relatively high level of diversity and endemism because of the island’s location, age, isolation and varied topography, despite the only 2% of native forest remaining… The various organisations, public and private, have been working hard since the middle of the 1900s to preserve and improve the situation. The area under native restoration has increased by over 500% since 2010.
Many animal species have disappeared since the discovery of Mauritius, probably around the end of the 15th century. We have only one native mammal still alive in Mauritius, the Mauritian bat, nine endemic birds and 11 reptile species. The birds and reptiles are mostly found in National Parks and on Round Island and Ile aux Aigrettes which are under the aegis of the government preservation programme and the Mauritian Wildlife Foundation (MWF).
Some parts of the coastal regions in Mauritius also have a rich biodiversity, including marshlands, that need to be preserved. NGOs, such as REEF Conservation, are constantly implementing preservation and awareness programmes, with the support of the public in general, private institutions and the government to save these precious zones!
Sources:
Britannica.com
greenfacts.org
Clearing House Mechanism for Biodiversity – chm.govmu.org